Transforming Waste into Resources: A Comprehensive Guide to Upcycling and Recycling
Related Articles: Transforming Waste into Resources: A Comprehensive Guide to Upcycling and Recycling
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Transforming Waste into Resources: A Comprehensive Guide to Upcycling and Recycling. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Transforming Waste into Resources: A Comprehensive Guide to Upcycling and Recycling

The world’s waste problem is a pressing issue, generating immense environmental and economic burdens. However, amidst the challenge lies an opportunity: the potential to transform waste into valuable resources. This practice, known as upcycling and recycling, offers a sustainable solution by repurposing discarded materials into new, functional products. This article delves into the diverse world of waste-based creations, highlighting the benefits and providing practical insights for individuals and communities.
A Spectrum of Upcycling and Recycling:
Upcycling and recycling are distinct yet interconnected approaches to waste management. Recycling involves transforming waste into new materials of the same or lower quality, while upcycling elevates the value of discarded items by creating products of higher quality or use. Both methods offer significant advantages:
- Environmental Protection: Recycling and upcycling reduce the demand for virgin materials, thereby minimizing the extraction of natural resources, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resource Conservation: By reusing discarded materials, these practices conserve valuable resources like timber, metals, and minerals, ensuring their availability for future generations.
- Waste Reduction: Recycling and upcycling effectively reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, alleviating the burden on landfills and minimizing environmental pollution.
- Economic Benefits: The creation of new products from waste can generate employment opportunities, stimulate local economies, and reduce reliance on imported materials.
- Social Impact: Upcycling and recycling foster a sense of community and responsibility, encouraging individuals to participate in sustainable practices and promote environmental awareness.
A Diverse Palette of Waste-Based Creations:
The possibilities for transforming waste are limitless, spanning a wide range of materials and applications. Here are some notable examples:
1. Paper and Cardboard:
- Paper Mache: A versatile technique utilizing shredded paper mixed with paste to create sculptures, masks, and decorative items.
- Cardboard Furniture: Sturdy and stylish furniture pieces can be constructed from cardboard, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials.
- Cardboard Boxes: Reused boxes can be transformed into storage solutions, organizers, and even playhouses for children.
- Paper Beads: Paper strips can be rolled into beads, offering a unique and sustainable jewelry option.
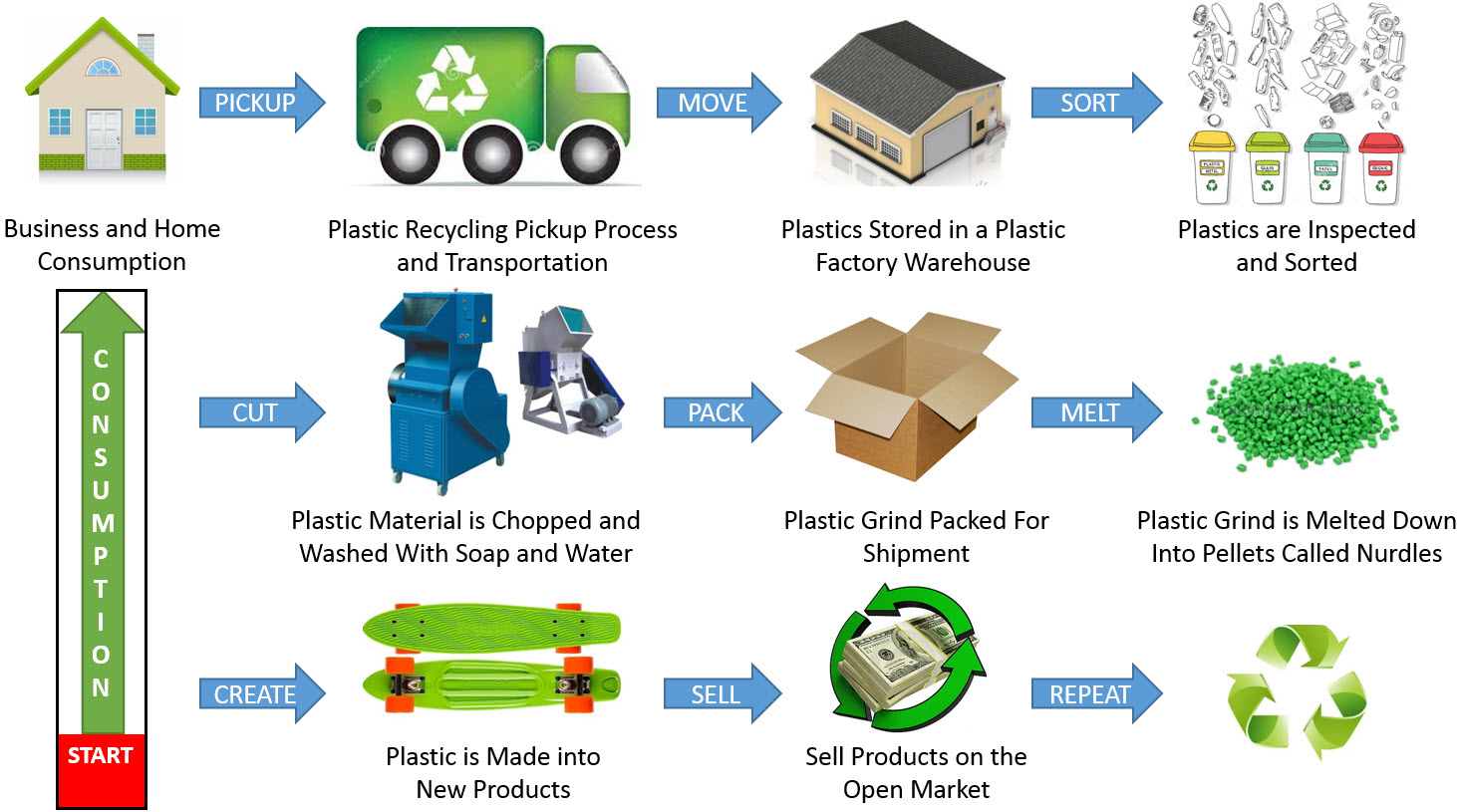
2. Plastic:
- Plastic Bottles: Plastic bottles can be repurposed into planters, water bottles, and even building materials.
- Plastic Bags: Recycled plastic bags can be woven into mats, baskets, and even clothing.
- Plastic Lids: Plastic lids can be used to create mosaics, decorative tiles, and even jewelry.
- Plastic Straws: Instead of discarding them, plastic straws can be used to create colorful and unique decorations.
3. Glass:
- Glass Bottles: Glass bottles can be transformed into decorative vases, candle holders, and even wind chimes.
- Glass Jars: Glass jars can be used for storage, crafts, and even as decorative elements.
- Broken Glass: Broken glass can be crushed and used as a decorative aggregate in landscaping or incorporated into mosaic art.
4. Metal:
- Tin Cans: Tin cans can be repurposed into planters, storage containers, and even wind chimes.
- Metal Scraps: Metal scraps can be melted down and recast into new products, or used for artistic creations.
5. Textiles:
- Old Clothes: Old clothes can be repurposed into bags, quilts, and even furniture upholstery.
- Fabric Scraps: Fabric scraps can be used to create patchwork quilts, decorative pillows, and even jewelry.
6. Wood:
- Scrap Wood: Scrap wood can be used to create furniture, decorative items, and even small structures.
- Pallet Wood: Pallet wood can be repurposed into furniture, shelves, and even wall art.
7. Organic Waste:
- Food Waste: Food waste can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil amendments for gardens.
- Yard Waste: Yard waste can be composted or used as mulch to improve soil health and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
8. Electronic Waste:
- E-Waste Recycling: Electronic waste can be recycled to recover valuable metals and other materials.
- Upcycling Electronic Components: Reusable electronic components can be incorporated into new projects, fostering innovation and reducing waste.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What are the challenges of upcycling and recycling?
- Market Demand: The demand for recycled and upcycled products can fluctuate, making it challenging for businesses to invest in these practices.
- Material Sorting and Processing: Sorting and processing waste can be labor-intensive and costly, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and durability of upcycled products can be a challenge, requiring rigorous testing and quality control measures.
- Consumer Acceptance: Consumers may be hesitant to purchase upcycled products due to perceptions of lower quality or aesthetic appeal.
2. How can I get involved in upcycling and recycling?
- Reduce Your Waste: Start by reducing your overall waste generation through mindful consumption and composting.
- Recycle Properly: Familiarize yourself with local recycling guidelines and ensure you are sorting your waste correctly.
- Upcycle at Home: Explore upcycling projects using discarded materials found around your home.
- Support Local Upcycling Businesses: Purchase products from local businesses that specialize in upcycling and recycling.
- Advocate for Policy Changes: Support policies that encourage waste reduction, recycling, and upcycling initiatives.
3. What are some tips for successful upcycling?
- Clean and Prepare Materials: Thoroughly clean and sanitize all materials before using them in upcycling projects.
- Consider Functionality: Ensure that the upcycled product is functional and meets your intended use.
- Embrace Creativity: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different materials and techniques to create unique and innovative designs.
- Safety First: Always prioritize safety when working with tools and materials.
- Share Your Creations: Inspire others by showcasing your upcycled creations and sharing your knowledge.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Through Waste Transformation
Transforming waste into resources through upcycling and recycling is not merely an environmental necessity but a creative and innovative opportunity. By embracing these practices, we can reduce our environmental footprint, conserve valuable resources, and foster a more sustainable future. From simple household projects to large-scale industrial operations, the possibilities for transforming waste are boundless, offering a path towards a circular economy where resources are valued and utilized to their full potential. By embracing this transformative approach, we can build a world where waste is not a burden but a source of opportunity, innovation, and prosperity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Waste into Resources: A Comprehensive Guide to Upcycling and Recycling. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!